Internal Combustion Engine Timing System and Timing Belt Care
Introduction
The timing system in an internal combustion engine plays a crucial role in ensuring proper engine performance. It synchronizes the movement of various components, allowing valves to open and close at the right time. In this article, we’ll explore the key aspects of the timing system, focusing on timing belts and their maintenance.
Internal Combustion Engine Timing System
- Ignition Timing:
- In a spark ignition internal combustion engine, ignition timing determines when the spark plug fires relative to the piston position and crankshaft angle during the compression stroke.
- Advancing or retarding the spark ensures efficient combustion and prevents issues like engine knock or wasted sparks.
- Modern engines use computer-controlled ignition systems, while older engines rely on mechanical distributors.
- Valve Timing:
- The camshaft controls valve timing, ensuring precise opening and closing of intake and exhaust valves.
- Proper valve timing affects power, efficiency, and emissions.
- Variable valve timing (VVT) systems adjust valve timing dynamically based on engine conditions.
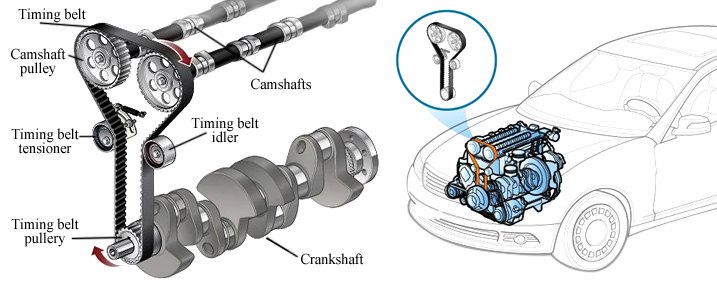
Timing Belts: Purpose and Function
- What Is a Timing Belt?
- A timing belt is a toothed rubber belt that connects the crankshaft and camshaft(s).
- It synchronizes their rotation, ensuring valves open and close at the right time during the engine cycle.
- Signs of Wear and Replacement Intervals:
- Inspect the timing belt for cracks, frayed edges, or missing cogs.
- Common symptoms of a failing timing belt include engine misfiring and difficulty starting.
- Replace the timing belt every 60,000 to 100,000 miles (consult your owner’s manual).
- Importance of Proper Tension and Alignment:
- Correct belt tension and alignment prevent premature failure.
- Use a take-up system to apply tension (inside or back side of the belt).
- Sonic tension meters provide accurate measurements.
- Proper alignment during installation is essential for belt longevity.
Timing Belt vs. Timing Chain
- Some engines use timing chains (metal) instead of rubber belts.
- Chains are quieter and have longer lifespans.
- Check your owner’s manual to determine which your vehicle uses.
Conclusion
Maintaining your timing belt is crucial for engine health. Regular inspections, proper tension, and timely replacements ensure reliable performance and prevent costly repairs. Remember, a well-maintained timing system keeps your engine running smoothly and safely on the road!
For more detailed information, consult your vehicle’s manual or seek professional advice from a mechanic123